The Difference Between HMOs and PPOs in Individual Health Insurance
When it comes to individual health insurance, there are various plan options available, each with its own features and benefits. Among the most common types of health insurance plans are Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs) and Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs). Understanding the differences between these two types of plans is crucial for individuals seeking the best coverage to suit their healthcare needs and budget. In this post, we will delve into the details of HMOs and PPOs, highlighting their key characteristics, pros, and cons, to help individuals make informed decisions about their health insurance options.
Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs):
Health Maintenance Organizations, or HMOs, are managed care plans that offer comprehensive healthcare coverage through a network of healthcare providers. HMOs focus on preventive care and coordination of medical services, aiming to keep costs low and promote better health outcomes for their members.
Health Maintenance Organizations, or HMOs, are managed care plans that offer comprehensive healthcare coverage through a network of healthcare providers. HMOs focus on preventive care and coordination of medical services, aiming to keep costs low and promote better health outcomes for their members.
Key Features of HMOs
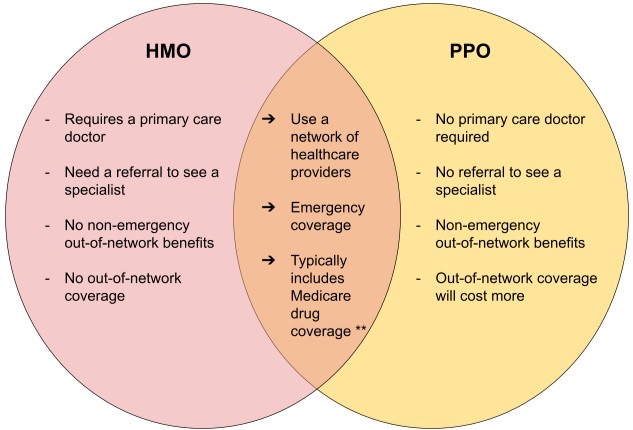
Primary Care Physicians (PCPs): One of the central elements of an HMO is the requirement for members to choose a Primary Care Physician (PCP). The PCP serves as the gatekeeper and coordinates all the member’s healthcare needs. If specialist care is required, the PCP provides a referral.
In-Network Providers: HMOs have a network of doctors, hospitals, and other healthcare facilities that members must use to receive the highest level of coverage. In most cases, HMOs do not provide coverage for out-of-network services, except in emergencies or other specific situations.
Low Out-of-Pocket Costs: HMOs typically have lower out-of-pocket costs, such as copayments and deductibles, compared to other types of plans. However, members may need to pay a copayment for each visit to their PCP or specialist.
Comprehensive Coverage: HMOs cover a wide range of preventive services, including immunizations, screenings, and wellness visits. They are also known for emphasizing preventive care and disease management programs.
Advantages of HMOs
Lower Costs: HMOs generally have lower premiums and out-of-pocket costs compared to PPOs, making them an attractive option for individuals on a budget.
Care Coordination: The coordination of care by a PCP can lead to better management of chronic conditions and reduced fragmentation of healthcare services.
Preventive Care: HMOs place a strong emphasis on preventive care, helping to identify health issues early and promote overall well-being.
Disadvantages of HMOs
Limited Choice of Providers: HMO members must use in-network providers, which can limit their choice of healthcare professionals and facilities.
Referral Requirement: In an HMO, members must obtain a referral from their PCP to see a specialist, which can create delays in accessing specialized care.
Out-of-Network Coverage: HMOs generally do not cover out-of-network services, except in emergencies, which can be a drawback for individuals who prefer more flexibility in choosing their providers.
Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs):
Preferred Provider Organizations, or PPOs, are also managed care plans, but they offer more flexibility and a broader network of providers compared to HMOs. PPOs allow members to seek care from both in-network and out-of-network providers, although the level of coverage and cost-sharing may vary.
Key Features of PPOs:
No PCP Requirement: Unlike HMOs, PPOs do not require members to choose a Primary Care Physician. Members have the freedom to see any healthcare provider without a referral.
In-Network and Out-of-Network Coverage: PPOs offer coverage for both in-network and out-of-network services. While using in-network providers is encouraged for cost-saving benefits, members can still receive partial coverage for services obtained out-of-network.
Higher Out-of-Pocket Costs: PPOs generally have higher premiums and out-of-pocket costs compared to HMOs. However, members may have lower copayments and deductibles when using in-network providers.
Flexibility: PPOs provide more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers, making them suitable for individuals who prefer to see specialists without going through a PCP.
Advantages of PPOs:
Provider Choice: PPOs offer a broader network of providers, allowing members to choose from a larger pool of healthcare professionals and facilities.
No Referrals Needed: PPO members can directly access specialists without needing referrals, making it more convenient for those with specific healthcare needs.
Out-of-Network Coverage: PPOs provide partial coverage for out-of-network services, which can be beneficial for individuals who prefer to use specific providers not available in-network.
Disadvantages of PPOs:
Higher Costs: PPOs generally have higher premiums and out-of-pocket costs compared to HMOs, which can be a deterrent for individuals on a tight budget.
Balance Billing: When using out-of-network providers, PPO members may be subject to balance billing, which means they could be responsible for paying the difference between the provider’s charge and the amount covered by the insurance company.
Overutilization: The greater flexibility of PPOs may lead to overutilization of healthcare services, potentially driving up overall healthcare costs.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this post is based on general knowledge and may not be up-to-date or applicable to specific insurance products or regulations in your jurisdiction. Insurance policies and regulations can vary widely, so it’s essential to research and verify information with local authorities or insurance providers.
FAQs about HMOs and PPOs
What is an HMO?
Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) is a type of managed care health insurance plan that provides coverage through a network of healthcare providers. HMOs typically require members to choose a Primary Care Physician (PCP) and obtain referrals for specialist care.
What is a PPO?
Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) is another type of managed care health insurance plan that offers more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers. PPOs have both in-network and out-of-network coverage options, and members can see specialists without referrals.
What is the main difference between HMOs and PPOs?
The main difference lies in provider choice and referrals. HMOs require members to use in-network providers and obtain referrals from a PCP to see specialists, while PPOs allow members to choose from a broader network of providers and see specialists without referrals.
Which one is more affordable, an HMO or a PPO?
Generally, HMOs tend to be more affordable in terms of premiums and out-of-pocket costs compared to PPOs. However, the cost difference can vary based on the specific insurance plan, location, and individual healthcare needs.
HMOs and PPOs fall under which type of healthcare organization
HMOs and PPOs fall under the category of managed care healthcare organizations.